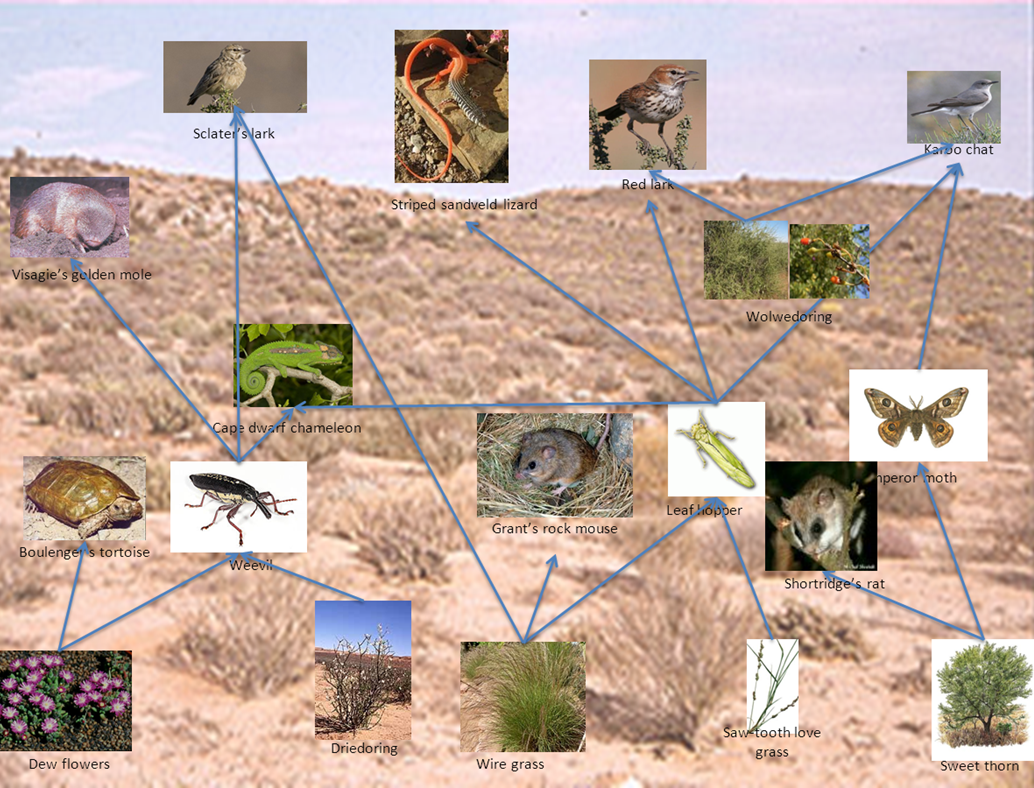
Animals In The Desert Food Chain

Sixth graders examine the prairie food chain while designing a rescue strategy for an endangered species.
Animals in the desert food chain. It eats nuts and berries plants It also eats fish animals. Then the primary consumers which are the herbivores eat the producers. A stream reef side of a pool field and woodland are all instances of an ecosystem.
Of course the animals herbivores carnivores or omnivores depend totally on the plants the foundation of the food chain for survival. Dung beetles eat animal feces. Detritivores are organisms that eat nonliving plant and animal remains.
Simultaneously the plants depend totally on the unpredictable desert environment. The producers are the plants cactus Creosote Bushed Thorn Acacras and many others. There is less variety within the community of organisms relative to tropical biomes or even the temperate rainforest biome of BC in the biosphere as the conditions are much harsher.
It includes abiotic and organic components through which nutrients are cycled and power circulations. The small rodents and insects and lizards eat the plants. The hawk will receive the energy of the snake rat and sagebrush.
They compare their strategy to that of a professional conservation expert. These animals are eaten by larger insects lizards and also snakes. Only about 2 Kilocalories per square meter per year are stored in their bodies.
In the Mojave the desert kit fox is one of the secondary consumers that feeds on cottontail. It can live up to 2000 years and can grow to about 24 feet wide. The food chain below shows this very food chain that was described above.