Food Chain Definition Ecology

A food chain is basically made up of producers and consumers.
Food chain definition ecology. In a community which has producers consumers and decomposers the energy flows in a specific pathway. The food chain describes who eats whom in the wild. Food ecology is the science which looks at the food production process and assesses the impact each stage of the process has on how plants and animals relate.
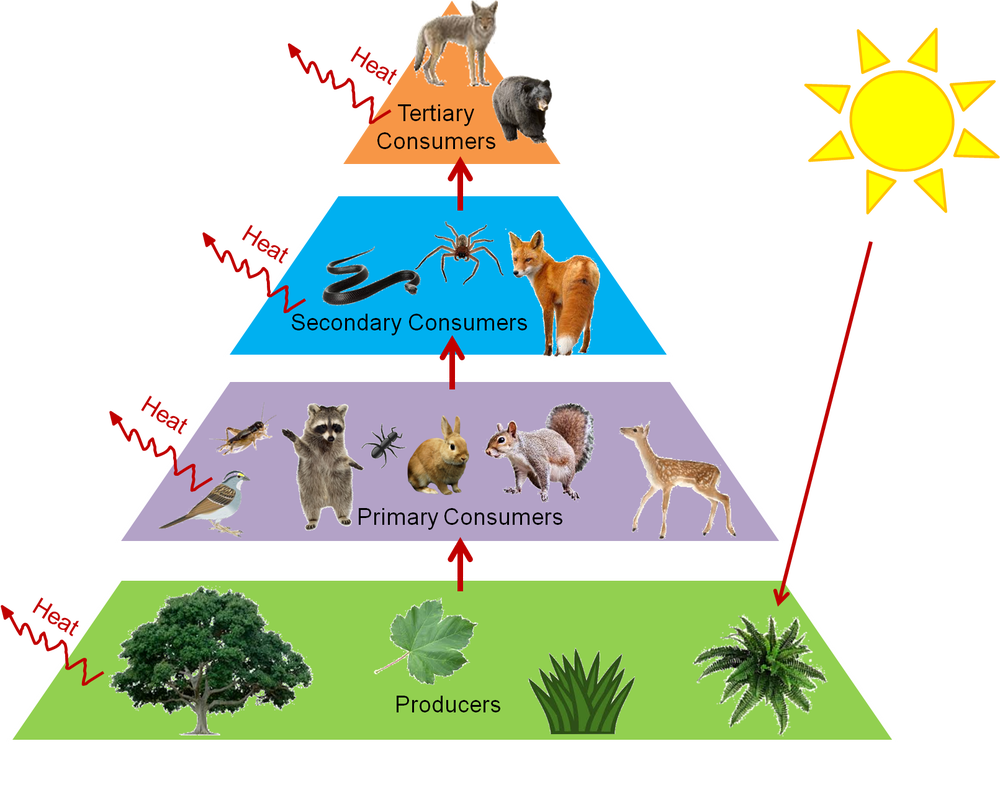
The sun is the initial source of energy which provides energy for everything on the planet. That is they can form one of the links in a food chain. For example grass produces its own food from sunlight.
Carl Linnaeus in an ecologically important essay The Economy of Nature Linnaeus Latin 1749. These easy recipes are all you need for making a delicious meal. Food chain definition ecology.
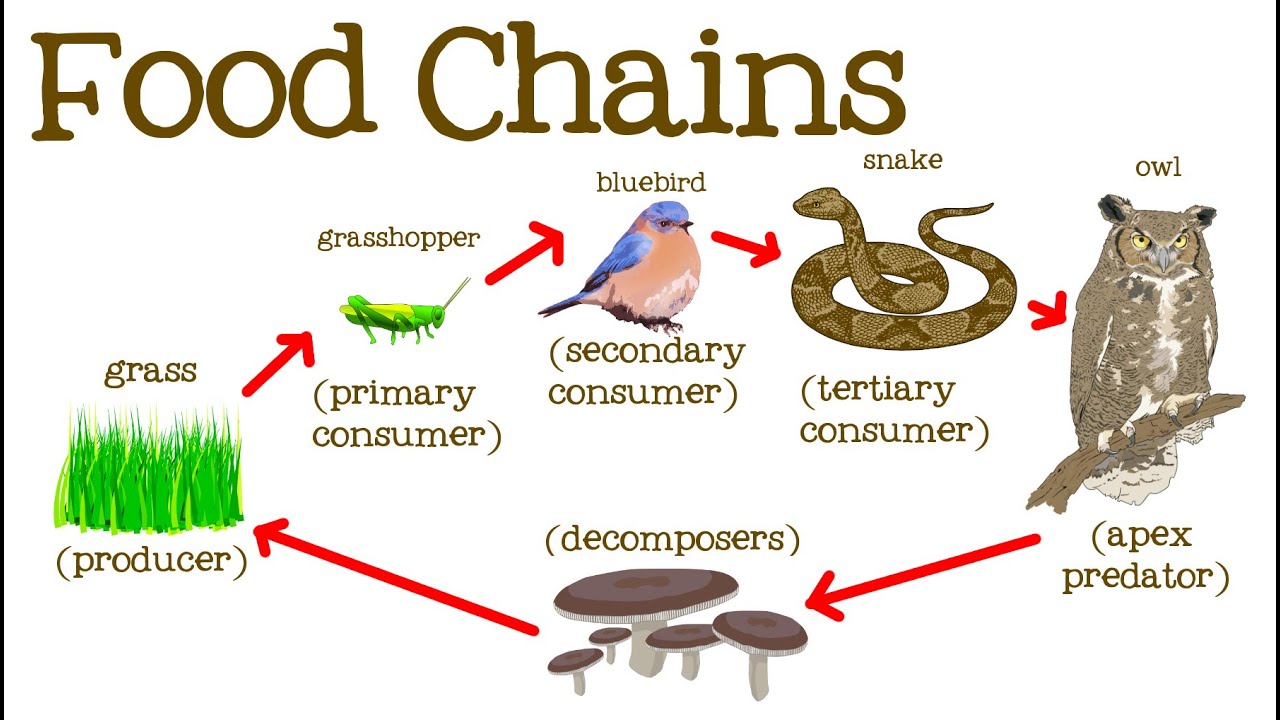
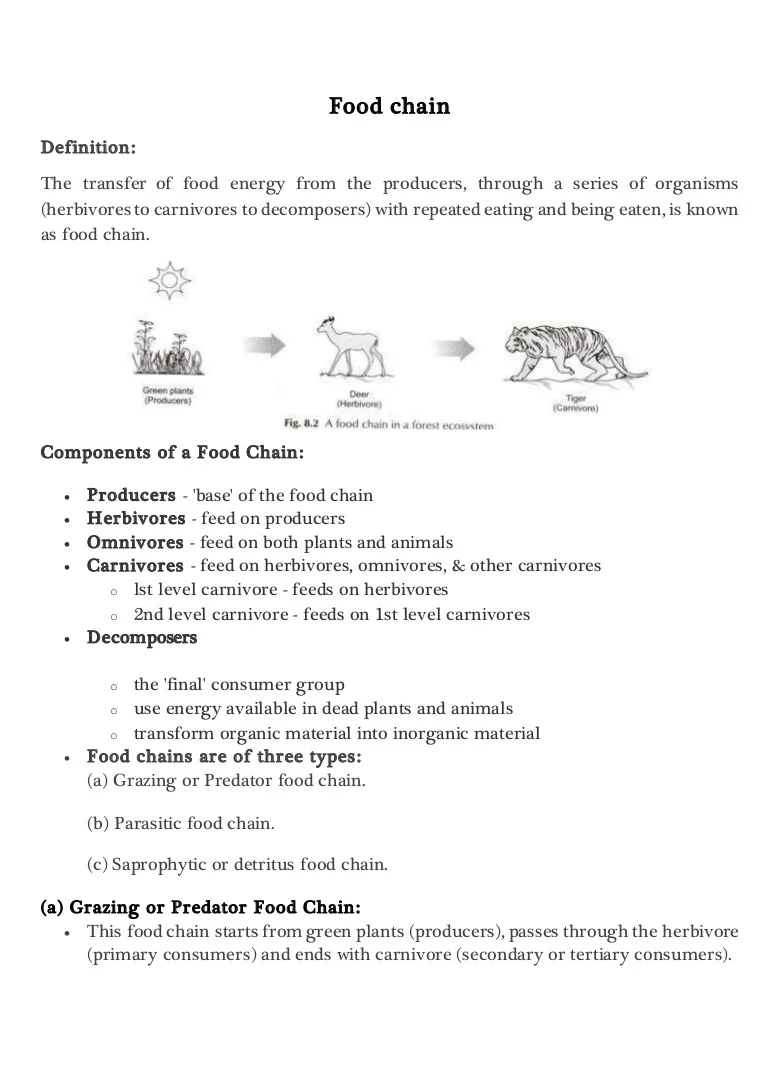
This occurs when one organism consumes another organism. A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms such as grass or trees which use radiation from the sun to make their food and ending at apex predator species like grizzly bears or killer whales detritivores like earthworms or woodlice or decomposer species such as fungi or bacteriaa food chain also shows how the organisms. Flow of energy in an ecosystem is one way process.
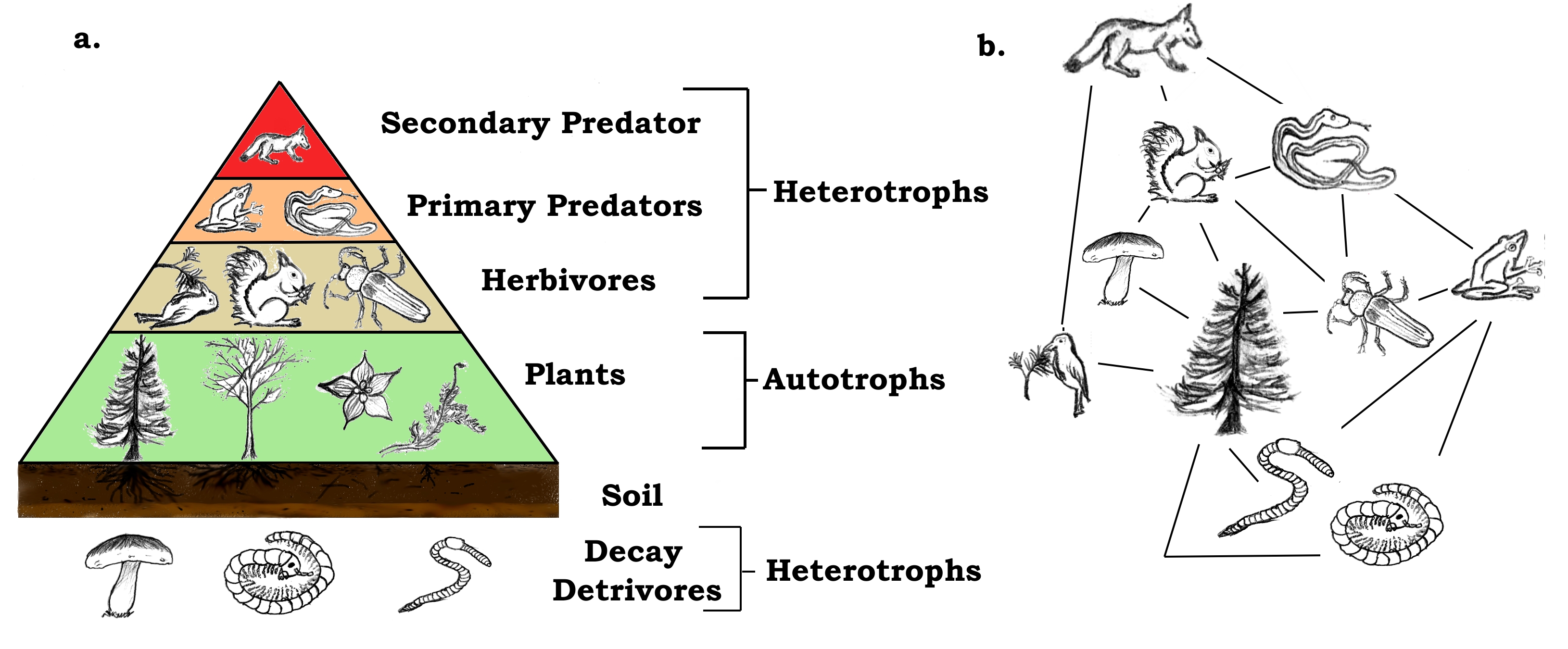
The pattern of eating and being eaten forms a linear chain called food chain. It begins with producer organism follows the chain and ends with decomposer organism. The term food chain describes the order in which organisms or living things depend on each other for food.
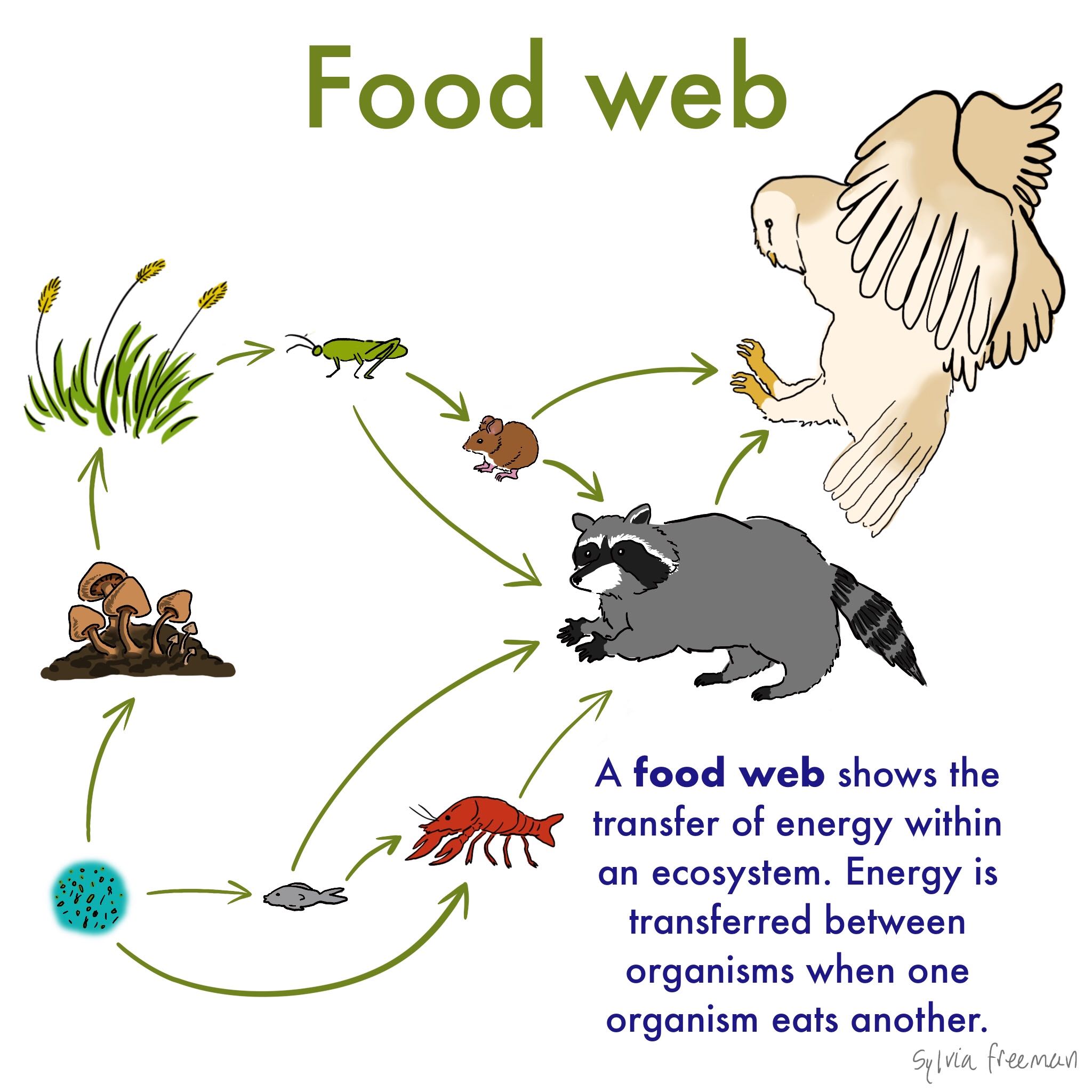
The food chain consists of four major parts. A food web shows multiple food chains multiple relationships and connections. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred from one organism to the other.